Cybersecurity Tips For Businesses
Cybersecurity tips for businesses: Protecting Your Company from Cyber Threats dives into the essential strategies and practices that businesses need to implement to safeguard their data and operations from potential cyber threats. In today’s digital age, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is paramount for the success and longevity of any business.
From understanding the importance of cybersecurity to securing network infrastructure, this guide covers a range of topics to equip businesses with the knowledge and tools needed to stay protected in the online landscape.
Importance of Cybersecurity for Businesses

In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is more important than ever for businesses of all sizes. Protecting sensitive data and information from cyber threats is crucial to maintaining trust with customers, safeguarding financial assets, and preserving the reputation of the business.
Examples of Cyber Threats, Cybersecurity tips for businesses
- Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals send deceptive emails to employees to trick them into revealing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts files on a company’s network, demanding payment for decryption.
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to customer or employee data, leading to potential identity theft or financial loss.
Potential Consequences of a Cybersecurity Breach
- Financial Loss: Businesses can incur significant financial losses due to the costs of recovering from a cyber attack, legal fees, and fines.
- Reputation Damage: A cybersecurity breach can tarnish the reputation of a business, leading to loss of customers and trust.
- Legal Consequences: Failure to protect customer data can result in legal action, fines, and regulatory penalties.
Best Practices for Securing Business Data
In today’s digital age, securing sensitive business data is of utmost importance to protect against cyber threats and data breaches. Implementing key best practices can help businesses safeguard their valuable information and maintain trust with their customers.
The Importance of Encryption
Encryption plays a critical role in protecting data by converting it into a secure code that can only be deciphered with the correct key. This ensures that even if unauthorized users gain access to the data, they will not be able to read or use it without the encryption key. Implementing encryption for both data at rest and data in transit is essential for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of business information.
- Utilize strong encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to protect sensitive data.
- Implement end-to-end encryption for communications and secure data storage to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly update encryption protocols and keys to stay ahead of potential security vulnerabilities.
The Role of Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are essential components of a robust data security strategy. Weak passwords are easy targets for cybercriminals, while multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing sensitive information.
- Encourage employees to create complex passwords that include a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Enforce password rotation policies to ensure that passwords are regularly updated and not reused across multiple accounts.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all user accounts, especially those with access to critical business systems and data.
Employee Training and Awareness

Employee training and awareness are crucial aspects of maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture within any organization.
Significance of Educating Employees
- Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, making them a critical component of overall cybersecurity strategy.
- Training employees on cybersecurity best practices can help prevent costly data breaches and cyber attacks.
- By educating staff members, businesses can create a more security-conscious workforce that is equipped to identify and respond to potential threats.
Tips for Conducting Effective Training Sessions
- Make training sessions interactive and engaging to keep employees interested and attentive.
- Provide real-life examples and case studies to illustrate the importance of cybersecurity in a practical context.
- Include hands-on exercises and simulations to allow employees to practice responding to potential security incidents.
Importance of Creating a Culture of Awareness
- Encouraging a culture of cybersecurity awareness helps employees understand that security is everyone’s responsibility, not just the IT department’s.
- Regularly reinforce the importance of cybersecurity through ongoing training, communication, and reminders.
- Reward employees who demonstrate good security practices and actively contribute to the organization’s security efforts.
Secure Network Infrastructure: Cybersecurity Tips For Businesses

In today’s digital age, securing network infrastructure is crucial for businesses to protect sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks. By implementing robust security measures, businesses can safeguard their networks from potential threats and minimize the risk of data breaches.
Securing Wi-Fi Networks, Routers, and Firewalls
- Change default passwords: Ensure that default passwords for Wi-Fi networks, routers, and firewalls are changed to strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable encryption: Use WPA3 encryption for Wi-Fi networks to encrypt data transmissions and protect sensitive information from being intercepted.
- Update firmware regularly: Keep routers and firewalls up to date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities and enhance overall network security.
Benefits of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
- Real-time threat detection: Intrusion detection systems can identify suspicious activities on the network and alert administrators to potential security breaches.
- Preventive measures: Intrusion prevention systems can automatically block malicious traffic and prevent cyber attacks from compromising the network.
- Enhanced network visibility: Implementing these systems provides businesses with greater visibility into network traffic and helps identify and mitigate security risks proactively.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
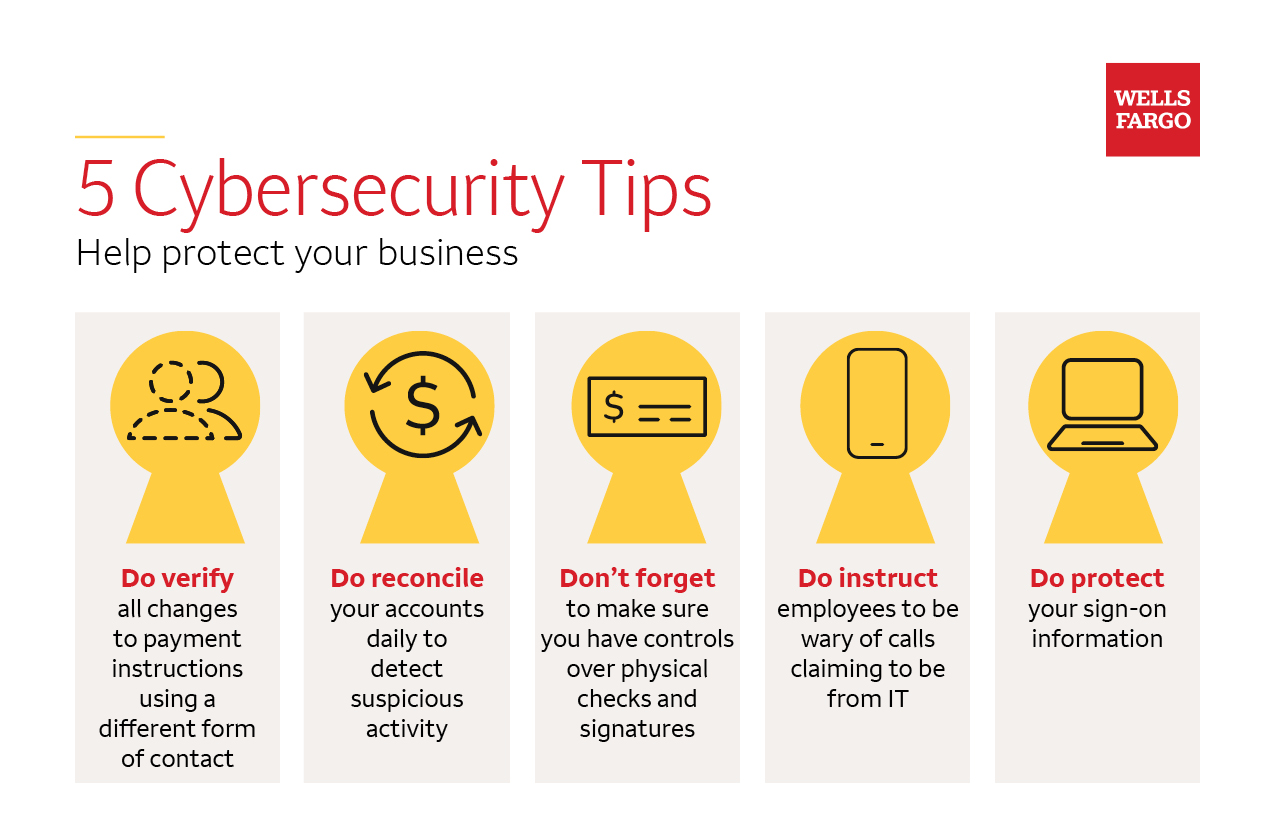
Regular software updates and patch management are crucial aspects of maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture for businesses. By ensuring that all software is up to date, organizations can protect themselves against vulnerabilities and potential cyber attacks.
Developing a Patch Management Strategy
Implementing a robust patch management strategy is essential for businesses to stay ahead of potential security threats. Here are some tips to help develop an effective patch management plan:
- Establish a centralized patch management system to track and deploy updates across all devices and software applications.
- Regularly monitor vendor websites, security advisories, and industry news for information on the latest patches and updates.
- Prioritize critical patches and schedule regular maintenance windows to apply updates without disrupting business operations.
- Test patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to production systems to ensure compatibility and minimize potential issues.
- Automate patch deployment processes where possible to streamline updates and reduce the risk of human error.
By proactively managing software updates and patches, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and data loss.
Risks of Running Outdated Software
Running outdated software and unpatched systems can expose businesses to a wide range of security risks, including:
- Increased vulnerability to malware and cyber attacks that exploit known weaknesses in outdated software.
- Potential data breaches and loss of sensitive information due to unpatched security vulnerabilities.
- Compliance violations and legal repercussions for failing to maintain secure systems and protect customer data.
- Disruption of business operations and financial losses resulting from cybersecurity incidents and data breaches.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
In today’s digital age, data is the lifeblood of businesses, making it crucial to have a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan in place.
Importance of Data Backup
Backing up your data is like having an insurance policy against cyber threats and unexpected disasters. It ensures that in case of a cyber incident or data loss, your business can quickly recover and resume operations without significant downtime or loss of critical information.
Creating a Robust Backup Plan
- Regularly schedule automated backups of all important data, including customer information, financial records, and sensitive documents.
- Store backups in secure, offsite locations to prevent loss in the event of physical damage to your primary data storage.
- Implement encryption to protect your backup data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Consider using cloud-based backup solutions for added convenience and scalability.
Role of Testing Backup Systems
Testing your backup systems regularly is crucial to ensure their reliability and effectiveness in the event of a data loss situation. By simulating various scenarios and restoring data from backups, you can identify any weaknesses or gaps in your backup plan and address them proactively.
FAQ Summary
Why is cybersecurity crucial for businesses?
Cybersecurity is crucial for businesses to protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and safeguard against financial losses resulting from cyber attacks.
How can businesses secure their network infrastructure?
Businesses can secure their network infrastructure by implementing firewalls, securing Wi-Fi networks, and utilizing intrusion detection systems to monitor and prevent unauthorized access.
What role does employee training play in cybersecurity?
Employee training is essential in creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness, educating staff on best practices, and reducing the risk of human error leading to security breaches.